

Note that the triangle provided in the calculator is not shown to scale while it looks equilateral (and has angle markings that typically would be read as equal), it is not necessarily equilateral and is simply a representation of a triangle. As can be seen from the triangles above, the length and internal angles of a triangle are directly related, so it makes sense that an equilateral triangle has three equal internal angles, and three equal length sides. Similar notation exists for the internal angles of a triangle, denoted by differing numbers of concentric arcs located at the triangle's vertices. Tick marks on the edge of a triangle are a common notation that reflects the length of the side, where the same number of ticks means equal length.
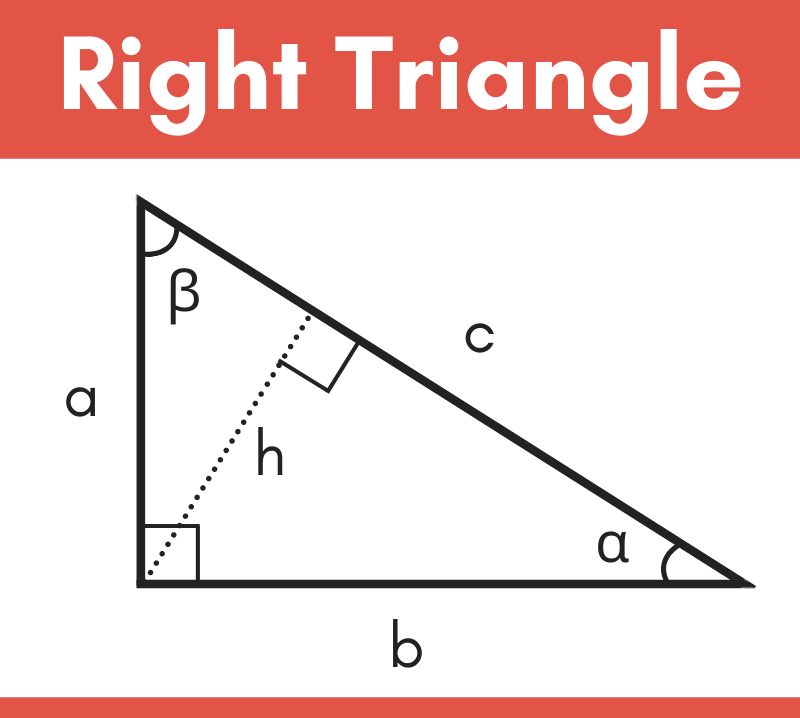
When none of the sides of a triangle have equal lengths, it is referred to as scalene, as depicted below. For example, a triangle in which all three sides have equal lengths is called an equilateral triangle while a triangle in which two sides have equal lengths is called isosceles. Furthermore, triangles tend to be described based on the length of their sides, as well as their internal angles. Hence, a triangle with vertices a, b, and c is typically denoted as Δabc. A triangle is usually referred to by its vertices. A vertex is a point where two or more curves, lines, or edges meet in the case of a triangle, the three vertices are joined by three line segments called edges. When radians are selected as the angle unit, it can take values such as pi/2, pi/4, etc.Ī triangle is a polygon that has three vertices. Please provide 3 values including at least one side to the following 6 fields, and click the "Calculate" button. Home / math / triangle calculator Triangle Calculator


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
